Securing printers
Securing network connections
Configuring TCP/IP port access settings
You can control your network device activities by configuring your device to filter out traffic on specific network connections. Protocols (such as FTP, HTTP, and Telnet) can be disabled.
Port filtering on devices disables network connections individually. When a port is closed, a device does not respond to traffic on the specified port whether the corresponding network application is enabled.
We recommend closing any ports that you do not plan to use under standard operation by clearing them.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
TCP/IP
>
TCP/IP Port Access
.
-
Enable the access to the TCP/IP ports.
-
Click
Save
.
Note:
For more information on each port, contact your system administrator.
Configuring IP Security settings
Apply IP Security (IPsec) between the printer and the workstation or server to secure traffic between the systems with a strong encryption. The printers support IPsec with preshared keys (PSKs) and certificates. You can use both options simultaneously.
When using PSK authentication, printers are configured to establish a secure IPsec connection with up to seven other systems. The printers and systems are configured with a pass phrase that is used to authenticate the systems and to encrypt the data.
When using the CA certificate authentication, printers are configured to establish a secure IPsec connection with up to five systems or subnets. Printers exchange data securely with many systems, and the process is integrated with a PKI or CA infrastructure. Certificates provide a robust and scalable solution, without configuring or managing keys and pass phrases.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
IPSec
.
-
Select
Enable IPSec
.
-
Configure the following settings to specify the encryption and authentication methods of the printer:
-
Base Configuration
-
DH (Diffie-Hellman) Group Proposal
-
Proposed Encryption Method
Note:
This feature is enabled when Base Configuration is set to
Compatibility
.
-
Proposed Authentication Method
Note:
This feature is enabled when Base Configuration is set to
Compatibility
.
-
IPSec Device Certificate
-
Do one or more of the following:
-
From the Pre-Shared Key Authenticated Connections section, type the IP address of the client printer that you want to connect to the printer.
-
From the Certificate Authenticated Connections section, type the IP address of the client printer that you want to connect to the printer.
-
Click
Save
.
Notes:
-
If no CA certificates are added, then the default certificate is used.
-
If you are using PSK authentication, then type the corresponding key. Retain the key to use later when configuring client printers.
Configuring 802.1x authentication
Though normally associated with wireless devices and connectivity, 802.1x authentication supports both wired and wireless environments.
Notes:
-
If using digital certificates to establish a secure connection to the authentication server, then configure the certificates on the printer before changing 802.1x authentication settings. For more information, see
Managing certificates
.
-
Make sure that all printers on the same network using 802.1x are supporting the same EAP authentication type.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
802.1x
.
-
From the 802.1x Authentication section, do the following:
-
Select
Active
.
-
Type the login name and password that the printer uses to log in to the authentication server.
-
Select
Validate Server Certificate
.
Note:
Server certificate validation is necessary when using Transport Layer Security (TLS), Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP), and Tunneled Transport Security Layer (TTLS).
-
Select
Enable Event Logging
.
Warning—Potential Damage:
To reduce flash part wear, use this feature only when necessary.
-
In the 802.1x Device Certificate list, select the digital certificate that you want to use.
Note:
If only one certificate is installed, then
default
is the only option that appears.
-
From the Allowable Authentication Mechanisms section, select one or more authentication protocols.
-
EAP-MD5, EAP-MSCHAPv2, LEAP, and PEAP require a login name and password.
-
EAP-TLS requires a login name, CA certificate, and signed printer certificate.
-
EAP-TTLS requires a login name and password and CA certificate.
-
In the TTLS Authentication Method menu, select the authentication method to use.
-
Click
Save
.
Setting the restricted server list
You can configure printers to connect only from a list of specified TCP/IP addresses. This action blocks all TCP connections from other addresses, protecting the printer against unauthorized printing and configuring.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
TCP/IP
.
-
In the Restricted Server List field, type up to 50 IP addresses, separated by commas, that are allowed to make TCP connections.
-
Click
Save
.
Managing devices remotely
Using HTTPS for printer management
To restrict the access of the printer Embedded Web Server to HTTPS only, turn off the HTTP port, leaving the HTTPS port (443) active. This action ensures that all communication with the printer using the Embedded Web Server is encrypted.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
TCP/IP
>
TCP/IP Port Access
.
-
Clear
TCP 80 (HTTP)
.
-
Click
Save
.
Setting up SNMP
Configuring SNMP versions 1 or 2c settings
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
SNMP
.
-
From the SNMP Versions 1 and 2c section, select
Enabled
>
Allow SNMP Set
.
-
In the SNMP Community field, type a name for the SNMP Community identifier. The default community name is
public
.
-
Select
Enable PPM MIB
(Printer Port Monitor MIB) to facilitate the automatic installation of printer drivers and other printing applications.
-
Click
Save
.
Configuring SNMP version 3 settings
Before you begin, disable SNMP versions 1 and 2c.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
SNMP
.
-
From the SNMP Version 3 section, select
Enabled
.
-
If necessary, configure the following by providing your
authentication credentials:
-
In the Authentication Hash menu, select the hash function
of your SNMP server.
-
In the Minimum Authentication Level, select
Authentication, Privacy
.
-
In the Privacy Algorithm menu, select the strongest setting
supported by your network environment.
-
Click
Save
.
Configuring SNMP traps
After configuring SNMP settings, you can customize which alerts are sent to the network management system by designating events (SNMP traps) that trigger an alert message.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Network/Ports
>
SNMP
>
Set SNMP Traps
.
-
In one of the IP Address fields, type the IP address of the network management server or monitoring station.
-
Select the conditions that you want to generate an alert.
-
Click
Save
.
Configuring security audit log settings
The security audit log lets you monitor security-related events on a device, including failed user authorization, successful administrator authentication, and Kerberos file uploads to a device. By default, security logs are stored on the device, but may also be transmitted to a network system log (syslog) server for processing or storage.
We recommend enabling audit in secure environments.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Security Audit Log
.
-
Do one or more of the following:
Activate security audit logging
Select
Enable Audit
.
Configure transmission to a network syslog server
This option lets you use both the remote syslog server and the internal logging.
-
Select
Enable Remote Syslog
.
-
Configure the Remote Syslog settings.
-
Remote Syslog Server
—Type the IP address or host name of the server.
-
Remote Syslog Port
—Type the port number used for the destination server. The default number is 514.
-
Remote Syslog Method
—Select
Normal UDP
to send log messages and events using a lower-priority transmission protocol. Otherwise, select
Stunnel
.
-
Remote Syslog Facility
—Select a facility code for events logged to the destination server. All events sent from the device are tagged with the same code to aid in sorting and filtering by network monitor or intrusion detection software.
-
Severity of Events to Log
—Select the priority level cutoff for logging messages and events. The highest severity is 0, and the lowest is 7. The selected severity level and anything higher are logged. For example, if you select
4 - Warning
, then severity levels 0–4 are logged.
-
Remote Syslog Non-Logged Events
—Send all events regardless of severity to the remote server.
Configure e-mail notification
Before you begin, make sure that the printer settings have been configured for e-mail.
-
In the Admin’s E-mail Address field, type one or more e-mail addresses, separated by commas.
-
Configure the notification settings.
-
E-mail Log Cleared Alert
—Send a notification when the Delete Log button is clicked.
-
E-mail Log Wrapped Alert
—Send a notification when the log becomes full and begins to overwrite the oldest entries.
-
Log Full Behavior
—Wrap over oldest entries or e-mail the log and then delete all entries.
-
E-mail % Full Alert
—Send a notification when log storage space reaches a certain percentage of capacity.
-
% Full Alert Level
—Specify how full the log must be before an alert is triggered.
-
E-mail Log Exported Alert
—Send a notification when the log file is exported.
-
E-mail Log Settings Changed Alert
—Send a notification when the log settings are changed.
-
Log Line Endings
—Specify how the log file terminates the end of each line.
-
Digitally Sign Exports
—Add a digital signature to each exported log file.
-
Click
Save
.
Managing security audit logs
-
To delete the syslog, in the Clear Log menu, click
Clear
.
-
To view or save the syslog, in the Export Log menu, select the file type, and then click
Export
.
Updating firmware
Printers inspect all downloaded firmware packages for required attributes before adopting and executing the packages. The firmware is packaged in a proprietary format and encrypted with a symmetric encryption algorithm through an embedded key that is known only to Lexmark. However, the strongest security measure comes from requiring all firmware packages to include multiple digital 2048-bit RSA signatures from Lexmark. If these signatures are not valid, or if the message logs indicate a change in firmware after the signatures were applied, then the firmware is discarded.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Device
>
Update Firmware
.
-
Do either of the following:
-
Browse to the firmware file, and then click
Upload
.
-
Click
Check for updates now
>
I agree, start update
.
Managing login methods
Restricting the access of guest account users
The guest account can use the printer without logging in. Control the guest account users from accessing the printer functions and applications, as well as managing the printer and its security options.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Public section, click
Manage Permissions
.
-
Select the access controls that the guest account can access. For more information, see
Understanding access controls
.
-
Click
Save
.
Using local accounts
Local accounts are stored in the printer memory and provide authentication-level security.
Creating local accounts
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Local Accounts section, click
Add
User
.
-
Select the type of authentication method that you want
the account to use when logging in to the printer.
-
User Name/Password
—Add
an account with a user name and password.
-
User Name
—Add
an account with a user name only.
-
Password
—Add
an account with a password only.
-
PIN
—Add an account
with a personal identification number (PIN) only.
-
From the User Information section, type the user information
and authentication credentials.
-
From the Permission Groups section, select one or more
groups.
-
Click
Save
.
Editing and deleting
local accounts
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Local Accounts section, click the authentication
method where the user account belongs to.
-
Click the user account that you want to edit or delete.
-
Do either of the following:
-
To edit the user account, update the user information,
and then click
Save
.
-
To delete the user account, click
Delete
User
.
Note:
To delete multiple user accounts, select the account, and then
click
Delete
.
Creating local account groups
Use groups to customize users’ access to applications and printer functions.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
Do either of the following:
Add a group when managing permissions
-
From the Local Accounts section, click
Manage Groups/Permissions
.
-
Click
Add Group
.
Add a group when creating or editing a user account
-
Create or edit a user account.
-
From the Permission Groups section, select
Add New Group
.
-
Type a unique group name.
-
From the Access Controls section, select the functions, menus, and applications that the group can access.
-
Click
Save
.
Notes:
-
To import access controls from another group, click
Import Access Controls
, and then select a group.
-
For more information on access controls, see
Understanding access controls
.
Editing or deleting local account groups
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Local Accounts section, click
Manage Groups/Permissions
.
-
Click the group, and then do either of the following:
Notes:
-
To import access controls from another group, click
Import Access Controls
, and then select a group.
-
To delete multiple groups, select the groups, and then click
Delete
.
-
For more information on access controls, see
Understanding access controls
.
Using LDAP or LDAP+GSSAPI
LDAP is a standards-based, cross-platform, extensible protocol that runs directly on top of the TCP/IP layer. It is used to access information stored in a specially organized information directory. It can interact with many different kinds of databases without special integration, making it more flexible than other authentication methods.
LDAP+GSSAPI is used when you want your transmission to be always secure. Instead of authenticating directly with the LDAP server, the user is first authenticated using Kerberos to obtain a Kerberos ticket. This ticket is presented to the LDAP server using the GSSAPI protocol for access. LDAP+GSSAPI is typically used for networks running Active Directory.
Notes:
-
LDAP+GSSAPI requires a Kerberos network account. For more information, see
Creating a Kerberos login method
.
-
Supported printers can store a maximum of eight unique LDAP or LDAP+GSSAPI login methods. Each method must have a unique name.
-
Administrators can create up to 32 user-defined groups that apply to each unique login method.
-
LDAP and LDAP+GSSAPI relies on an external server for authentication. If the server is down, then users are not able to access the printer using LDAP or LDAP+GSSAPI.
-
To help prevent unauthorized access, log out from the printer after each session.
Creating an LDAP or LDAP+GSSAPI login method
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Network Accounts section, click
Add Login Method
>
LDAP
.
-
Select the authentication type.
-
Configure the settings.
General Information
-
Setup Name
—Type a unique name for the LDAP network account.
-
Server Address
—Type the IP address or the host name of the LDAP server.
-
Server Port
—Enter the port where LDAP queries are sent.
Note:
If you are using SSL, then use port
636
. Otherwise, use port
389
.
-
Required User Input
—Select the required LDAP authentication credentials used when logging in to the printer. This setting is available only in the LDAP setup.
-
Use Integrated Windows Authentication
—Select one of the following:
-
Do not use
-
Use if available
—Use Windows operating system authentication credentials, if available.
-
Require
—Use only Windows operating system authentication credentials.
Note:
This setting is available only in the LDAP+GSSAPI setup.
Device Credentials
-
Anonymous LDAP Bind
—Bind the printer with the LDAP server anonymously. This option is applicable only if your LDAP server allows anonymous binding. Enabling this option does not require you to provide authentication credentials. This option is available only in the LDAP setup.
-
Use Active Directory Device Credentials
—Use user credentials and group designations that are pulled from the existing network comparable to other network services. This option is available only in the LDAP+GSSAPI setup.
-
If
Anonymous LDAP Bind
or
Use Active Directory Device Credentials
is disabled, then provide the authentication credentials used to bind the printer with the LDAP server.
Advanced Options
-
Use SSL/TLS
—If the LDAP server requires SSL, then select
SSL/TLS
.
-
Require Certificate
—If the LDAP server requires a certificate, then select
Yes
.
-
Userid Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute to search for when authenticating users’ credentials. The default value is
sAMAccountName
, which is common in a Windows operating system environment. For other directories, you can type
uid
,
cn
, or a user-defined attribute. For more information, contact your system administrator.
-
Mail Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ e-mail addresses. The default value is
mail
.
-
Fax number Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ fax number. The default value is
facsimiletelephonenumber
.
-
Full Name Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ full names. The default value is
cn
.
-
Home Directory Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ home directory. The default value is
homeDirectory
.
-
Group Membership Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute required for group search. The default value is
memberOf
.
-
Search Base
—The node in the LDAP server where user accounts reside. You can type multiple search bases, separated by commas.
Note:
A search base consists of multiple attributes separated by commas, such as cn (common name), ou (organizational unit), o (organization), c (country), and dc (domain).
-
Search Timeout
—Enter a value from 5 to 30 seconds or 5 to 300 seconds, depending on your printer model.
-
Follow LDAP Referrals
—Search the different servers in the domain for the logged-in user account.
Search Specific Object Classes
-
person
—Search the “person” object class.
-
Custom Object Classes
—Type the name of the custom object class to search.
Note:
A maximum of three custom object classes can be searched. Type the other object class in the other Custom Object Class field.
Address Book Setup
The following settings are used to configure the address book used when scanning to an e-mail address.
-
Displayed Name
—Select the LDAP attribute that you want to show on the address book.
-
Max Search Results
—Type the maximum search results shown on the address book.
-
Use user credentials
—Use the logged-in user credentials to connect to the LDAP server.
-
Search Attributes
—Select LDAP attributes used as search filters.
-
Custom Attributes
—Type LDAP custom attributes used as search filters.
-
Click
Save and Verify
.
Editing or deleting LDAP or LDAP+GSSAPI login methods
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Network Accounts section, click the LDAP or LDAP+GSSAPI login method.
-
Do either of the following:
-
To edit the login method, update the LDAP or LDAP+GSSAPI settings, and then click
Save and Verify
.
-
To delete the login method, click
Delete LDAP
.
Using Kerberos
You can use this login method by itself or in conjunction with the LDAP+GSSAPI login method.
Notes:
-
Only one Kerberos configuration file can be saved in the printer memory. This configuration file can apply to multiple realms and Kerberos Domain Controllers.
-
Uploading another configuration file or updating the Kerberos settings overwrites the saved configuration file.
-
If you want to delete a Kerberos file, then delete first the LDAP+GSSAPI login method that is using the file.
-
You must anticipate the different types of authentication requests the Kerberos server may receive, and configure the configuration file to handle the requests.
-
Kerberos relies on an external server for authentication. If the server is down, then users are not able to access the printer using Kerberos.
-
To help prevent unauthorized access, log out from the printer after each session.
Creating a Kerberos login method
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Network Accounts section, click
Add Login Method
>
Kerberos
.
-
Do one of the following:
Create a simple Kerberos configuration file
From the Generate Simple Kerberos File section, configure the following:
-
KDC Address
—Type the IP address or host name of the KDC IP.
-
KDC Port
—Enter the port number used by the Kerberos server.
-
Realm
—Type the realm used by the Kerberos server. The realm must be typed in uppercase.
Import a Kerberos configuration file
In the Import Kerberos File field, browse to the krb5.conf file.
-
If necessary, from the Miscellaneous Settings section, configure the following settings:
-
Click
Save and Verify
.
Setting the date and time
When using Kerberos authentication, make sure that the time difference between the printer and the domain controller does not exceed five minutes. You can manually update the date and time settings or use the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to sync the time with the domain controller automatically.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Device
>
Preferences
>
Date and Time
.
Configuring manually
Note:
Configuring the date and time manually disables NTP.
-
From the Configure section, in the Manually Set Date and Time field, enter the appropriate date and time.
-
Select the date format, time format, and time zone.
Note:
If you select
(UTC+user) Custom
, then specify the offset values for UTC (GMT) and DST.
Configuring NTP
-
From the Network Time Protocol section, select
Enable NTP
, and then type the IP address or host name of the NTP server.
-
If the NTP server requires authentication, then in the Enable Authentication menu, select
MD5 key
.
-
Depending on your printer model, either enter the key ID and password, or browse to the file containing the NTP authentication credentials.
-
Click
Save
.
Using Active Directory
You can use this login method by itself or in conjunction with the LDAP+GSSAPI login method.
Notes:
-
Only one Kerberos configuration file can be saved in the printer memory. This configuration file can apply to multiple realms and Kerberos Domain Controllers.
-
You must anticipate the different types of authentication requests the Kerberos server may receive, and configure the configuration file to handle the requests.
-
Uploading another configuration file or updating the Kerberos settings overwrites the saved configuration file.
-
Active Directory relies on an external server for authentication. If the server is down, then users are not able to access the printer using Active Directory.
-
To help prevent unauthorized access, log out from the printer after each session.
Creating an Active Directory login method
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Network Accounts section, click
Add Login Method
>
Active Directory
.
-
Configure the settings.
-
Domain
—Type the realm or domain name of the Active Directory server.
-
User Name
—Type the name of the user that can authenticate to the Active Directory.
-
Password
—Type the password of the user.
-
Organizational Unit
—Type the organizational unit attribute the user belongs to.
-
Click
Join Domain
.
Editing or deleting an Active Directory login method
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Network Accounts section, click the Active Directory login method.
-
Do either of the following:
-
To delete the login method, click
Unjoin Domain
.
-
Configure the following settings, and then click
Save and Verify
.
General Information
-
Setup Name
—Type a unique name for the Active Directory login method.
-
Server Address
—Type the IP address or the host name of the LDAP server.
-
Server Port
—Enter the port where queries are sent.
-
Required User Input
—Select the required authentication credentials when logging in to the printer.
-
Use Integrated Windows Authentication
—Select one of the following:
-
Do not use
-
Use if available
—Use Windows operating system authentication credentials, if available.
-
Require
—Use only Windows operating system authentication credentials.
Device Credentials
-
Use Active Directory Device Credentials
—Use user credentials and group designations that are pulled from the existing network comparable to other network services.
-
If
Use Active Directory Device Credentials
is disabled, then provide the authentication credentials used to bind the printer with the Active Directory server.
-
Device Username
—Type the fully qualified DN of a user registered to the Active Directory server.
-
Device Realm
—The Active Directory domain name.
-
Device Password
—Type the password for the user.
Advanced Options
-
Use SSL/TLS
—If the LDAP server requires SSL, then select
SSL/TLS
.
-
Require Certificate
—If the LDAP server requires a certificate, then select
Yes
.
-
Userid Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute to search for when authenticating users’ credentials. The default value is
sAMAccountName
, which is common in a Windows environment. For other directories, you can type
uid
,
cn
, or a user-defined attribute. For more information, contact your system administrator.
-
Mail Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ e-mail addresses. The default value is
mail
.
-
Fax number Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ fax number. The default value is
facsimiletelephonenumber
.
-
Full Name Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ full names. The default value is
cn
.
-
Home Directory Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute that contains the users’ home directory. The default value is
homeDirectory
.
-
Group Membership Attribute
—Type the LDAP attribute required for group search. The default value is
memberOf
.
-
Search Base
—The node in the LDAP server where user accounts reside. You can type multiple search bases, separated by commas.
Note:
A search base consists of multiple attributes separated by commas, such as cn (common name), ou (organizational unit), o (organization), c (country), and dc (domain).
-
Search Timeout
—Enter a value from 5 to 30 seconds or 5 to 300 seconds, depending on your printer model.
-
Follow LDAP Referrals
—Search the different servers in the domain for the logged-in user account.
Search Specific Object Classes
-
person
—Search the “person” object class.
-
Custom Object Classes
—Type the name of the custom object class to search.
Note:
A maximum of three custom object classes can be searched. Type the other object class in the other Custom Object Class field.
Address Book Setup
The following settings are used to configure the address book used when scanning to an e-mail address:
-
Displayed Name
—Select the LDAP attribute that you want to show on the address book.
-
Max Search Results
—Type the maximum search results shown on the address book.
-
Use user credentials
—Use the logged-in user credentials to connect to the LDAP server.
-
Search Attributes
—Select LDAP attributes used as search filters.
-
Custom Attributes
—Type LDAP custom attributes used as search filters.
Creating LDAP, LDAP+GSSAPI, Kerberos, or Active Directory groups
Use groups to customize user access to applications and printer functions.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
From the Network Account section, click
LDAP
,
LDAP+GSSAPI
,
Kerberos
, or
Active Directory
as the login method.
-
Click
Manage Groups
>
Add Group
.
-
Do either of the following:
Search for the group name or user name
-
Select how you want to search for the group in your LDAP server.
-
Depending on the search scope selected, type the group name or user name.
-
Click
Search
.
-
Select the group that you want to add.
-
Click
Add Selected
.
Add a group manually
-
Click
Manual Add
.
-
In the Group Name field, type the name of the group.
-
In the Group Identifier field, type the LDAP identifier for the group.
-
Click
Submit
.
-
Select the group, and then from the Access Controls section, select the functions, menus, and applications that the group can access.
-
Click
Save
.
Notes:
-
To import access controls from another group, click
Import Access Controls
, and then select a group.
-
For more information on access controls, see
Understanding access controls
.
Editing or deleting LDAP, LDAP+GSSAPI, or Active Directory groups
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Methods
.
-
Click the LDAP, LDAP+GSSAPI, or Active Directory login method, and then click
Manage Groups
.
-
Click the group, and then do either of the following:
Notes:
-
To import access controls from another group, click
Import Access Controls
, and then select a group.
-
To delete multiple groups, select the groups, and then click
Delete
.
-
For more information on access controls, see
Understanding access controls
.
Understanding access controls
Access controls let you limit users’ access to functions, applications, and printer management.
Note:
Some access controls are available only in some printer models.
Function Access
The following access controls modify users’ access to available printer functions:
-
Access Address Book in Apps
—Use Address Book from eSF applications that support it.
-
Manage Shortcuts
—Access the Manage Shortcuts menu, and enable the “Save as Shortcut” option available in the Copy, E-mail, Fax, and FTP functions.
-
Modify Address Book
—Enable the Search Address Book option available in the E-mail, Fax, and FTP functions when accessed from the printer home screen.
-
Create Profiles
—Create profiles for printing, copying, scanning, e-mailing, or faxing.
-
Manage Bookmarks
-
Flash Drive Print
—Print from a flash drive.
-
Flash Drive Color Printing
—Print in color from a flash drive.
-
Flash Drive Scan
—Scan to a flash drive.
-
Copy Function
—Use the copy function.
-
Copy Color Printing
—Copy documents in color.
-
Color Dropout
—Specify the color to drop during scanning and copying, and to adjust the dropout setting for each color threshold. If a user authentication fails for a protected scan or copy job, then the Color Dropout function is not used even if it is enabled.
-
E-mail Function
—Use the e-mail function.
-
Fax Function
—Use the fax function. If this function is disabled, then:
-
All analog fax functions and the fax server are disabled.
-
The fax icon is removed.
-
No fax-related intervention-required messages appear on the printer display.
-
The printer does not answer incoming calls or print driver faxes.
Note:
The Embedded Web Server and control panel show fax-related settings even if this function is disabled.
-
FTP Function
—Scan to an FTP network folder from the printer home screen. The FTP icon is hidden by default. To show the FTP icon on the home screen, do the following:
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Device
>
Visible Home Screen Icons
.
-
Select
FTP
.
-
Release Held Faxes
—Enable the Held Faxes and Release Held Faxes options on the printer home screen.
-
Held Jobs Access
—Enable the Held Jobs and Search Held Jobs options on the printer home screen.
-
Use Profiles
—Restrict access to protected profiles. If a user accesses a protected profile, then the printer prompts for credentials to execute the profile. Enable this access control for the application that does not specify permission to access the profiles.
-
Cancel Jobs at the Device
—Cancel jobs from the printer home screen.
-
Change Language
—Enable the Change Language option on the printer home screen.
-
Internal Printing Protocol (IPP)
—Allow authenticated users to configure and use the IPP port.
-
Initiate Scans Remotely
—Allow authenticated users to initiate remote scanning.
-
B/W Print
—Allow authenticated users to print in black and white.
-
Color Print
—Allow authenticated users to print in color.
-
Network Folder - Scan
—Scan to a network folder.
Administrative Menus
The following access controls modify users’ access to the menus in the Embedded Web Server that are used to manage functions, applications, and security:
-
Security Menu
—Manage login methods and configure other security options.
-
Network/Ports Menu
—Configure network connections.
-
Paper Menu
—Configure the paper settings.
-
Reports Menu
—View reports.
-
Function Configuration Menus
—Configure the settings for the functions that are available in the printer.
-
Supplies Menu
—Manage printer supplies.
-
Option Card Menu
—Configure the option cards installed in the printer. This control is available only when an option card is installed.
-
SE Menu
—View diagnostic logs.
-
Manage Shortcuts
—Manage shortcuts that are available in the printer.
-
Address Book
—Manage the address book.
-
Device Menu
—Configure the printer firmware settings.
Device Management
The following access controls modify users’ access to use printer management options:
-
Remote Management
—Access the printer remotely.
-
Firmware Updates
—Update the printer firmware through any port.
-
Apps Configuration
—Configure the installed applications. If this control is enabled, then users can configure, start/stop, uninstall, and view logs of applications that are installed in the printer.
-
Operator Panel Lock
—Configure the locking function of the printer home screen. If this control is enabled, then users can lock and unlock the printer home screen.
-
Import / Export All Settings
—Import or export a printer settings file (ZIP and UCF) from the Embedded Web Server.
-
Out of Service Erase
—Clear all settings, applications, and pending jobs stored in the printer memory, or erase all data in the printer hard disk.
-
Embedded Web Server Access
—Control access to the Embedded Web Server. If this control is restricted, then access to the EWS requires login.
-
Cloud Services Enrollment
—Control access to the enrollment of the Lexmark cloud services.
Apps
-
New Apps
—Use applications from the printer home screen.
-
Card Copy
—Use Card Copy from the printer home screen.
-
Slideshow
—Use Slideshow from the printer home screen.
-
Change Wallpaper
—Use Change Wallpaper from the printer home screen.
-
Screen Saver
—Use Screen Saver from the printer home screen.
-
Forms and Favorites
—Use Forms and Favorites from the printer home screen.
-
Scan Center
—Use Scan Center from the printer home screen.
Managing certificates
Certificates are used when you want the printer to establish an SSL/TLS, IPsec, or 802.1x connection and to identify other devices on the network securely. Printers can also use these certificates for LDAP over SSL authentication and address book lookups.
Certificate Authorities (CA) are trusted locations established on the network that are required in secure environments. Otherwise, the default printer certificate is used to identify devices on the network.
Configuring printer certificate defaults
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Certificate Management
.
-
From the Device Certificates section, click
Configure Certificate Defaults
.
-
Configure the settings.
-
Friendly Name
—Type a unique name for the certificate.
-
Common Name
—Type the name for the printer.
Note:
If you want to use the printer host name, then leave this field blank.
-
Organization Name
—Type the name of the company or organization issuing the certificate.
-
Unit Name
—Type the name of the unit within the company or organization issuing the certificate.
-
Country/Region
—Type the country or region where the company or organization issuing the certificate is located.
-
Province Name
—Type the name of the province or state where the company or organization issuing the certificate is located.
-
City Name
—Type the name of the city where the company or organization issuing the certificate is located.
-
Subject Alternate Name
—Type the alternate name and prefix that conforms to RFC 2459. For example, type an IP address using the format
IP:1.2.3.4
, or a DNS address using the format
DNS:ldap.company.com
.
Note:
If your printer is using an IPv4 address, then leave this field blank.
-
Click
Save
.
Creating a printer certificate
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Certificate Management
.
-
From the Device Certificates section, click
Generate
.
-
Configure the settings. For more information, see
Configuring printer certificate defaults
.
-
Click
Generate
or
Generate and Download
.
Installing certificates manually
Before configuring Kerberos or domain controller settings, install the CA certificate used for domain controller validation. If you want to use chain validation for the domain controller certificate, then install the entire certificate chain. Each certificate must be in a separate PEM (.cer) file.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Certificate Management
.
-
From the Manage CA Certificates section, click
Upload CA
, and then browse to the PEM (.cer) file.
Sample certificate:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIE1jCCA76gAwIBAgIQY6sV0KL3tIhBtlr4gHG85zANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADBs
…
l3DTbPe0mnIbTq0iWqKEaVne1vvaDt52iSpEQyevwgUcHD16rFy+sOnCaQ==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-
Click
Save
.
Installing certificates automatically
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Certificate Management
>
Configure Certificate Auto Update
.
-
If you are prompted to join an Active Directory domain, then click
Join Domain
, and then type the domain information.
-
Select
Enable Auto Update
.
Note:
If you want to install the CA certificate without waiting for the scheduled run time, then select
Fetch Immediately
.
-
Click
Save
.
Viewing, downloading, and deleting a certificate
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Certificate Management
.
-
Select a certificate from the list.
-
Do one or more of the following:
-
Delete
—Remove a previously stored certificate.
-
Download To File
—Download or save the certificate as a PEM (.cer) file.
-
Download Signing Request
—Download or save the signing request as a .csr file.
-
Install Signed Certificate
—Upload a previously signed certificate.
Note:
To delete multiple certificates, select the certificates, and then click
Delete
.
Managing other access functions
Scheduling access to USB devices
In secure environments, devices can be configured to limit or disable the capabilities of USB host ports.
You can disable the front USB port using access control restrictions. Devices also have a rear USB port designed for card readers and human interface devices, such as a keyboard.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Schedule USB Devices
.
-
Select a device action, and then specify when the device performs the action.
-
Click
Save
.
Notes:
-
For each Disable schedule entry, create an Enable schedule entry to reactivate use of the USB host ports.
-
You can create multiple schedules.
Setting login restrictions
To prevent malicious access to a device, restrict the number of invalid login attempts and require a lockout time before letting users retry logging in.
Many organizations establish login restrictions for information assets such as workstations and servers. Make sure that device login restrictions also comply with organizational security policies.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Login Restrictions
.
-
Set the login restrictions.
-
Login failures
—Specify the number of times a user can attempt to log in before being locked out.
-
Failure time frame
—Specify how long a user can attempt to log in before lockout takes place.
-
Lockout time
—Specify how long the lockout lasts.
-
Web Login Timeout
—Specify how long a user may be logged in remotely before being logged out automatically.
-
Click
Save
.
Configuring confidential printing
Users printing confidential or sensitive information may use the confidential print option. This option lets print jobs remain in the print queue until the user enters a PIN on the printer control panel.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Confidential Print Setup
.
-
Enter an option for the following:
-
Max Invalid PIN
—Set the number of times an invalid PIN can be entered.
Notes:
-
When the limit is reached, the print jobs for that user name and PIN are deleted.
-
This setting appears only when a formatted, working printer hard disk is installed.
-
To turn off this setting, enter
0
.
-
Confidential Job Expiration
—Set the expiration time for confidential print jobs.
Notes:
-
Confidential held jobs are stored in the printer until they are released or deleted manually.
-
Changes in this setting do not affect the expiration time for confidential print jobs that are already in the printer memory or hard disk.
-
If the printer is turned off, then all confidential jobs held in the printer memory are deleted.
-
Repeat Job Expiration
—Set the expiration time for a repeat print job.
Note:
Repeat held jobs are stored in the printer memory for reprinting.
-
Verify Job Expiration
—Set the expiration time that the printer prints a copy before printing the remaining copies.
Note:
Verify jobs print one copy to check if it is satisfactory before printing the remaining copies.
-
Reserve Job Expiration
—Set the expiration time that the printer stores print jobs.
Note:
Reserve held jobs are automatically deleted after printing.
-
Require All Jobs to be Held
—Set the printer to hold all print jobs.
-
Keep duplicate documents
—Set the printer to print other documents with the same file name without overwriting any of the print jobs.
-
Click
Save
.
Enabling solutions LDAP settings
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Solutions LDAP Settings
.
-
Select one or more of the following:
-
Follow LDAP Referrals
—Search the different servers in the domain for the logged-in user account.
-
LDAP Certificate Verification
Note:
You need to restart the device for the changes to take effect.
-
Click
Save
.
Showing secured applications or functions on the home screen
By default, the secured applications or functions are hidden from the printer home screen.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Miscellaneous
.
-
In the Protected Features menu, select
Show
.
-
Click
Save
.
Enabling print permission
Use this feature for cost control. Whether users are allowed to print (color or black and white) or not depends on the user’s permission configuration. For more information, see
Managing login methods
.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Miscellaneous
.
-
Select
Print Permission
.
-
Click
Save
.
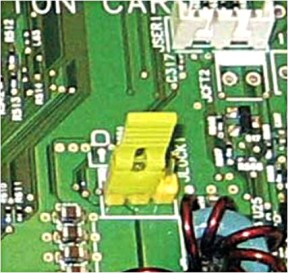
Enabling the security reset jumper
If the device is locked down because of a forgotten administrator password or lost network connectivity, then you can recover the device by resetting it. Access the controller board and move the reset jumper to cover the middle and exposed prongs.
Using a cable lock to secure access to the controller board ensures that the device is not maliciously reset.
Warning—Potential Damage:
Resetting the device deletes all customer data.
The secure reset feature requires specifying in the Embedded Web Server the effect of using the
security reset jumper
, which is on the controller board.
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Miscellaneous
.
-
In the Security Reset Jumper menu, select either of the following:
-
Enable “Guest” access
—Provide guests with full access control.
-
No Effect
—All protected access controls remain protected.
Warning—Potential Damage:
If this option is selected, then the device is locked down and you cannot access the security menus. To replace the device controller board and regain access to the security menus, a service call is required.
-
If necessary, enter a value in the
Minimum Password Length
field.
-
To enable the password or to reveal the PIN, click
Enable Password/PIN Reveal
.
-
Click
Save
.
Securing data
Configuring printer settings
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Device
>
Maintenance
.
-
Depending on the printer model, click
Config Menu
or
Configuration Menu
.
-
Configure the settings.
Note:
Some settings are available only in some printer models.
USB Configuration
-
USB PnP
—Change the USB driver mode of the printer to improve its compatibility with a personal computer.
-
USB Scan to Local
—Set whether the USB device driver enumerates as a USB Simple device (single interface) or as a USB Composite device (multiple interfaces).
-
USB Speed
—Set the USB port to run at full speed and disable its high-speed capabilities.
Tray Configuration
-
Tray Linking
—Specify if the tray is linked automatically.
-
Show Tray Insert Message
—Show a message about the tray status.
-
A5 Loading
—Specify the page orientation when loading A5 paper size.
-
Paper Prompts
—Set the paper source that the user fills when a prompt to load paper appears.
-
Envelope Prompts
—Set the paper source that the user fills when a prompt to load envelope appears.
-
Action for Prompts
—Set the printer to resolve paper- or envelope-related change prompts.
-
Multiple Universal Sizes
—Specify if the tray has multiple universal sizes.
Reports
Print reports about printer menu settings, status, and event logs.
-
Menu Settings Page
-
Event Log
-
Event Log Summary
Supply Usage and Counters
Fax Configuration
Print Configuration
-
Font Sharpening
—Set a text point-size value below which the high-frequency screens are used when printing font data. For example, if the value is 24, then all fonts sized 24 points or less use the high-frequency screens.
-
Print Density
—Adjust the toner density when printing documents.
-
Copy Density
—Adjust the toner density when copying documents.
Device Operations
-
Quiet Mode
—Set the printer to reduce the amount of noise that it makes when printing.
Note:
This setting slows down the overall performance of the printer.
-
Panel Menus
—Set the printer to show the control panel menus.
-
Safe Mode
—Set the printer to safe mode.
-
Minimum Copy Memory
—Specify the minimum copy memory of the device.
-
Clear Custom Status
—Erase all custom messages.
-
Clear all remotely-installed messages
—Erase all remotely installed messages.
-
Automatically Display Error Screens
—Set the printer to show error messages automatically.
-
Honor orientation on fast path copy
—Set the printer to determine if it will honor (or not) the page image orientation on a fast path copy.
Scanner Configuration
-
Scanner Manual Registration
-
Print Quick Test
—Print a Quick Test target page.
Note:
Make sure that the margin spacing on the target page is uniform all the way around the target. If it is not, then the printer margins may need to be reset.
-
Front ADF Registration
—Manually register the ADF after replacing the ADF, scanner glass, or controller board.
-
Rear ADF Registration
—Manually register the Rear after replacing the ADF, scanner glass, or controller board.
-
Flatbed Registration
—Manually register the scanner glass after replacing the ADF, scanner glass, or controller board.
-
Edge Erase
—Set the size, in millimeters, of the no-print area around a scan job.
-
ADF Edge Erase
-
Flatbed Edge Erase
-
ADF Deskew
—Set to adjust the front side and back side of the skew angles separately of the device.
Note:
The maximum amount of skew correction that can be applied to media of Letter/A4 width is 5%.
-
Disable Scanner
—Disable the scanner if it is not working properly.
-
Tiff Byte Order
—Set the byte order of a TIFF-formatted scan output.
-
Exact Tiff Rows Per Strip
—Set the RowsPerStrip tag value of a TIFF-formatted scan output.
-
Scanner Glass Cleaning Threshold
—Specify the number of scans before a user is prompted to clean the scanner glass.
Note:
The range of the number of scans is from 1000 to 3000.
-
Click
Save
.
Erasing printer memory
To erase volatile memory or buffered data in your printer, turn off the printer.
To erase nonvolatile memory or individual settings, printer and network settings, security settings, and embedded solutions, do the following:
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Device
>
Maintenance
.
-
From the Erase Printer Memory section, select
Sanitize all information on nonvolatile memory
.
-
If necessary, from the After erasing all nonvolatile memory section, select either
Start initial setup wizard
or
Leave printer offline
after erasing the printer memory.
-
Click
Start
.
Erasing printer storage drive
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Device
>
Maintenance
.
-
Depending on the storage drive that is installed on your printer, do either of the following:
-
Select
Sanitize all information on nonvolatile memory
, and then select either of the following:
Note:
The process to sanitize the hard disk can take from several minutes to more than an hour, making the printer unavailable for other tasks.
-
For intelligent storage drive (ISD), select
Cryptographically erase all user data on ISD
.
-
To further configure Erase Printer Memory settings, select the following:
-
Erase all printer and network settings
-
Erase all apps and app settings
-
Erase all shortcuts and shortcut settings
Note:
By default, on selecting Sanitize all information on nonvolatile memory, the above three settings get selected automatically.
-
Click
Start
.
Note:
Click
Reset
to change the configuration.
Configuring the intelligent storage drive
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Security
>
Miscellaneous
.
-
Select
Use Intelligent Storage Drive for User Data
to save the user data.
-
Click
Save
.
Restoring factory default settings
-
From the Embedded Web Server, click
Settings
>
Device
>
Restore Factory Defaults
.
-
Select the settings that you want to restore.
Note:
Some settings are available only in some printer models.
-
Restore printer settings—Restore all the printer settings to their default values.
-
Restore network settings—Restore all the network settings to their default values.
-
Restore fax settings—Restore all the fax settings to their default values.
-
Restore app settings—Restore all the app settings to their default values.
-
Click
Start
.
Statement of Volatility
|
Volatile memory
|
The printer uses standard random access memory (RAM) to buffer temporarily user data during simple print and copy jobs.
|
|
Nonvolatile memory
|
The printer may use two forms of non-volatile memory: EEPROM and NAND (flash memory). Both types store the operating system, printer settings, and network information. They also store scanner and bookmark settings and embedded solutions.
|
|
Hard disk storage drive
|
Some printers may have a hard disk drive installed. The printer hard disk is designed for printer-specific functionality. The hard disk lets the printer retain buffered user data from complex print jobs, form data, and font data.
|
|
Intelligent storage drive (ISD)
|
Some printers may have an ISD installed. ISD uses non-volatile flash memory to store user data from complex print jobs, form data, and font data.
|
Erase the content of any installed printer memory in the following circumstances:
-
The printer is decommissioned.
-
The printer hard disk or ISD is replaced.
-
The printer is moved to a different department or location.
-
The printer is serviced by someone from outside your organization.
-
The printer is removed from your premises for service.
-
The printer is sold to another organization.
Note:
To dispose a storage drive, follow the policies and procedures of your organization.