Understanding the automated certificate management feature
You can configure MVE to manage printer certificates automatically, and then install them to the printers through configuration enforcement. The following diagram describes the end-to-end process of the automated certificate management feature.
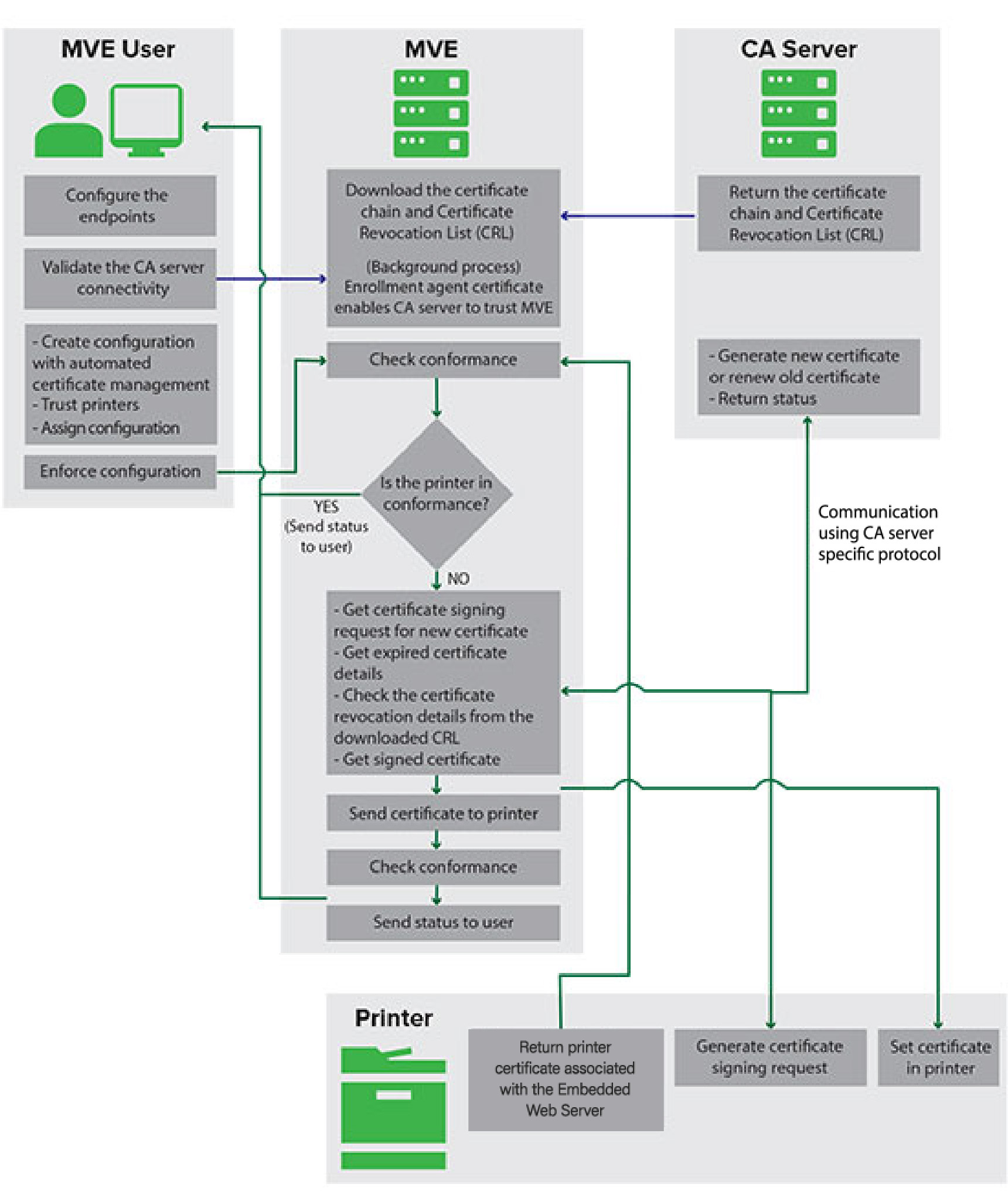
The certificate authority endpoints, such as the CA server and server address, must be defined in MVE.
The following CA servers are supported:
OpenXPKI CA—For more information, see Managing certificates using OpenXPKI Certificate Authority.
Microsoft CA Enterprise—Users can use either of the following protocols
Secure Certificate Encryption Protocol (SCEP)
Microsoft Certificate Enrollment Web Services (MSCEWS)
Note: MSCEWS is the recommended way to connect to Microsoft CA Enterprise server.
For more information, see the following topics:
Managing certificates using Microsoft Certificate Authority through SCEP
Managing certificates using Microsoft Certificate Authority through MSCEWS
The connection between MVE and the CA servers must be validated. During validation, MVE communicates with the CA server to download the certificate chain and the Certificate Revocation List (CRL). The enrollment agent certificate or test certificate is also generated. This certificate enables the CA server to trust MVE.
For more information on defining the endpoints and validation, see Configuring MVE for automated certificate management.
A configuration that is set to Use Markvision to manage device certificates must be assigned and enforced to the printer.
For more information, see the following topics:
During enforcement, MVE checks the printer for conformance.
For Default Device Certificate
The certificate is validated against the certificate chain downloaded from the CA server.
If the printer is out of conformance, a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is raised for the printer.
For Named Device Certificate
The certificate is validated against the certificate chain downloaded from the CA server.
MVE creates a self-signed named device certificate on the device.
If the printer is out of conformance, a CSR is raised for the printer.
Notes:
- MVE communicates with the CA server using supported protocol.
- The CA server generates the new certificate, and then MVE sends the certificate to the printer.
- If a named certificate exists in the printer, then a new named certificate is not created, but a CSR is raised for the printer.